OVERDALE
From: $ 752,382
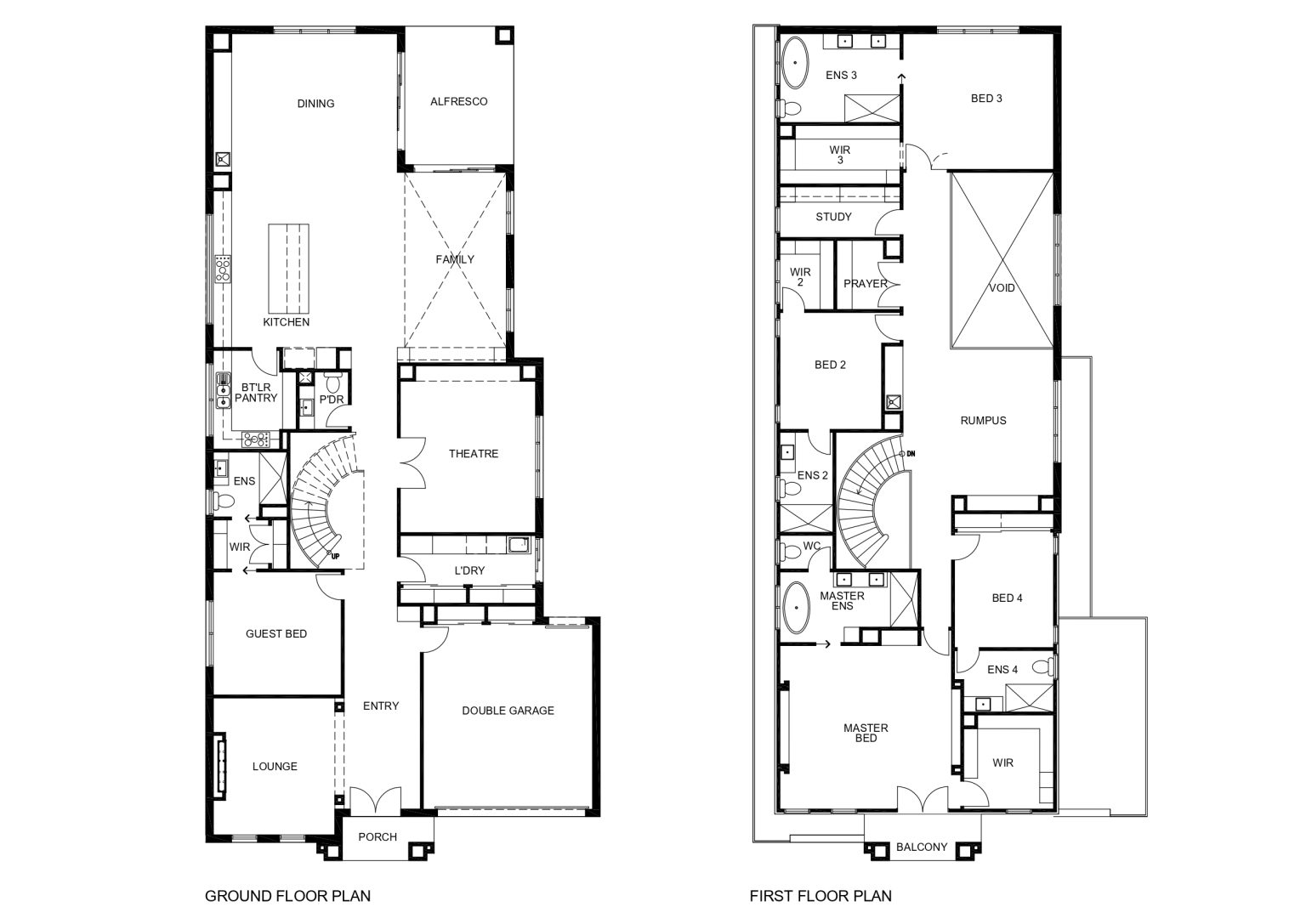
| Home Dimensions |
| House Area | 471.23 m2 (50.72 sqr.) |
| Garage Area | 36.20 m2 (3.90 sqr.) |
| Portico | 4.63 m2 (0.50 sqr.) |
| Alfresco | 15.93 m2 (1.71 sqr.) |
| Balcony | 5.01 m2 (0.54 sqr.) |
| Total Area | 533.01 m2 (57.37 sqr.) |
| House Width | 12.80 m |
| House Length | 27.08 m |
| Minimum Block Width | 14.00 m |
| Minimum Block Depth | 36.00 m |
| Room Dimensions |
| Family | 6.19m x 5.04m |
| Dining | 4.50m x 5.38m |
| Lounge | 4.45m x 3.95m |
| Theatre | 4.92m x 4.40m |
| Master Bed | 5.31m x 5.88m |
| Guest Bed | 4.00m x 4.16m |
| Bed 2 | 3.80m x 3.31m |
| Bed 3 | 4.41m x 4.89m |
| Bed 4 | 3.75m x 3.22m |
| Rumpus | 5.30m x 4.89m |
| Double Garage | 6.00m x 5.50m |